Microsoft announced its $26.2 billion acquisition of LinkedIn, the largest professional networking platform in the world, in June 2016. Microsoft’s expansion into the social networking and professional services industries was the goal of this one-of-a-kind transaction, one of the largest in the history of technology. The acquisition’s motives, strategic alignment between the two businesses, and subsequent impact on both organizations and the tech sector as a whole are examined in this case study.
Synopsis of LinkedIn:
Growth and Creation: In 2002, Reid Hoffman and a group of co-founders established LinkedIn. It sent off in 2003 as a stage for experts to interface, organization, and offer substance. By 2016, LinkedIn had more than 400 million individuals and had secured itself as a forerunner in proficient systems administration.
Business Strategy: Advertising, talent solutions, and premium subscriptions all contributed to LinkedIn’s revenue. The platform offered job postings, online courses, and a news feed that focused on professional content among other services.
Summary of Microsoft:
Company in the Technology Sector: Microsoft, which was founded in 1975 by Paul Allen and Bill Gates, was one of the largest and most diverse technology companies in the world. It was well-known for its software, which included the Office suite and the Windows operating system, as well as its Azure cloud services.
The Acquisition’s Strategic Motives:
Increasing Business Services:
Connectivity to Office 365: Integrating LinkedIn’s extensive professional network with its Office 365 suite was one of Microsoft’s primary motivations. This would enhance productivity tools like Outlook, Word, and Excel by incorporating LinkedIn’s professional data and insights. The goal of this integration was to give users personalized content, enhanced networking opportunities, and richer professional profiles.
Enhancing AI and the Cloud’s Capabilities:
Benefits from AI and data: Microsoft had the chance to improve its artificial intelligence (AI) capabilities thanks to LinkedIn’s extensive data on professionals and businesses. Microsoft could enhance its AI-driven products and services, such as Dynamics 365 and its enterprise resource planning (ERP) and CRM suite, by utilizing LinkedIn’s data.
Enhancing Professional and Social Networking:
Getting Started with Social Networking: Microsoft was able to strengthen its existing enterprise and productivity tools by acquiring a significant social networking company. LinkedIn’s attention on proficient systems administration lined up with Microsoft’s central goal to enable each individual and association in the world to accomplish more.
Incorporation and Key Drives:

Microsoft Products Integration:
Integration of LinkedIn and Office: Microsoft worked on incorporating LinkedIn features into its Office products following the acquisition. For instance, LinkedIn profile information was integrated into Outlook, giving users direct access to their inbox to view professional information about email contacts.
Development and Learning: Microsoft products were incorporated into LinkedIn Learning, an online education platform that offers professional courses, to improve organizations’ employee training and development.
Service Expansion on LinkedIn:
Expansion of Enterprise Software: LinkedIn continued to expand its enterprise solutions, such as LinkedIn Talent Solutions and LinkedIn Marketing Solutions, while it was owned by Microsoft. These administrations assisted organizations with ability procurement, promoting, and deals.
Center around Happy and Commitment: The news feed, LinkedIn Pulse, a content publishing platform, and video capabilities were all enhanced as a result of LinkedIn’s emphasis on content creation and engagement. This center expected to increment client commitment and time spent on the stage.
Growth in Revenue and Monetization:
Premium Subscriptions and Ad Revenue: LinkedIn’s adaptation systems were fortified, with an expanded spotlight on promotion income and premium memberships. The stage presented new promotion organizes and focusing on choices, utilizing Microsoft’s information and investigation capacities.
Results and Impact:
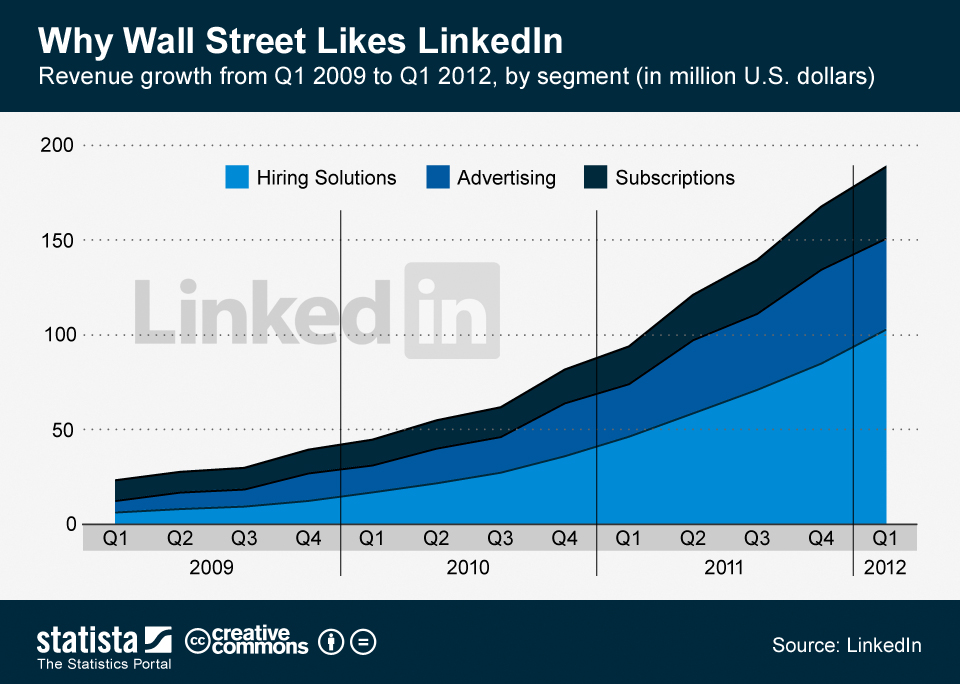
Financial Performance and Growth:
Increasing Revenue: LinkedIn’s revenue has increased significantly since the acquisition due to increased demand for its advertising, premium subscriptions, and talent solutions. This expansion was facilitated by the integration with Microsoft services and products.
Growth of Users: By 2021, LinkedIn’s user base will have reached more than 700 million. In addition to Microsoft’s support, the platform’s emphasis on professional content and networking attracted new users and increased engagement.
Synergies Strategically:
Enhanced Solutions for Businesses: Customers gained new value when LinkedIn’s data and insights were incorporated into Microsoft’s enterprise products, such as Dynamics 365 and Office 365. Microsoft’s position in the enterprise market was strengthened by this synergy.
Data Analytics and AI: Microsoft’s AI and data analytics capabilities were enhanced by LinkedIn’s data, making it possible to create services across a variety of Microsoft products that are more intelligent and personalized.
Positioning for Competition:
Differentiation from the Competition: By offering a unique combination of professional networking, productivity tools, and enterprise solutions, the acquisition set Microsoft apart from rivals like Google and Amazon. Microsoft’s position in the technology market was strengthened by this differentiation.
Considerations and Challenges:

Security and privacy of data:
Problems with Handling Data: There were concerns regarding the security and privacy of the user data, as with any acquisition involving a large amount of user data. In order to maintain user trust and comply with regulations, LinkedIn and Microsoft had to carefully navigate these issues.
Integration of Culture:
Culture in the workplace: It was difficult to integrate the cultures of two distinct organizations. Guaranteeing arrangement in mission, values, and functional practices was urgent for the progress of the coordination.
Conclusion:
Microsoft’s strategic acquisition of LinkedIn has demonstrated that it significantly strengthened both businesses’ offerings and market positions. Microsoft expanded its cloud and AI capabilities, strengthened its enterprise solutions, and entered the social networking space by utilizing LinkedIn’s professional network and data. Revenue has increased and user engagement has increased as a result of Microsoft’s successful integration of LinkedIn’s services with its products. In order to achieve long-term success in the technology sector, this case study highlights the significance of strategic acquisitions, the realization of synergies, and careful integration.



GIPHY App Key not set. Please check settings