The 2014 lead contamination of the drinking water supply in Flint, Michigan, sparked a significant public health and environmental catastrophe known as the Flint water crisis. This contextual analysis looks at the causes, effect, and reactions to the Stone water emergency, featuring the critical illustrations and suggestions for water the executives and general wellbeing.
Foundation and Setting
Authentic Setting:
Social and economic context: Flint, a city that has a long history of economic decline and population decline, was confronted with financial difficulties that prompted a series of decisions that affected the city’s water infrastructure. High rates of poverty and unemployment exacerbated the city’s economic challenges.
Administration and infrastructure: A series of administrative decisions regarding water management and infrastructure upkeep set in motion Flint’s water crisis. Major problems with the city’s water system, which is managed by state and local authorities, eventually led to contamination.
The Decision to Alter the Source of Water:

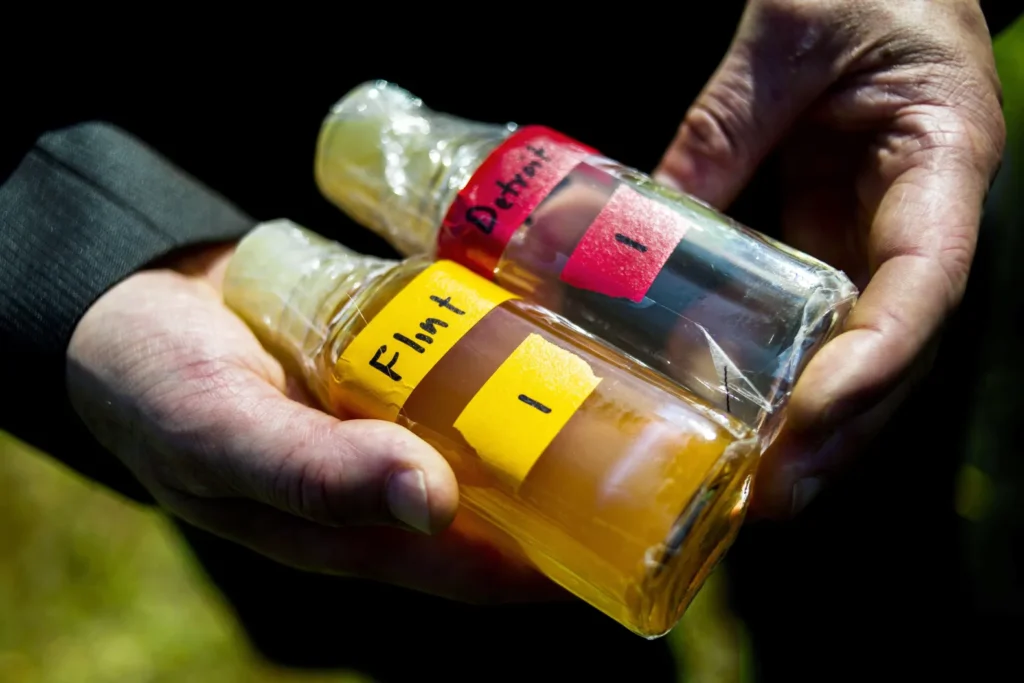
Starting Choice: As a cost-cutting measure while it waited for a new regional water supply system, Flint switched its water source from the Detroit Water and Sewerage Department (DWSD) to the Flint River in April 2014. The switch was made with the intention of saving money, but it had serious unintended consequences.
Consumption and Tainting: The Rock Stream water, being more destructive, started to dissolve the city’s maturing lead pipes, prompting the filtering of lead into the drinking water supply. The contamination issue got worse because the city didn’t use the right corrosion control measures.
Key Changes and Effects of the Public Health Crisis:
Contamination of Lead: Residents of Flint, particularly children, had elevated blood lead levels as a result of lead contamination in the drinking water. Lead poisoning can lead to serious health issues like behavioral problems, developmental delays, and cognitive impairments.
Wellbeing Impacts: As a result of the crisis, Flint’s population experienced an increase in lead-related health issues and a public health emergency. It is anticipated that the affected individuals, particularly children, will suffer significant and persistent long-term health effects.
Reaction and Mindfulness:
Advocacy and the Community: Through the efforts of local activists, journalists, and advocates for public health, the Flint water crisis attracted national and international attention. Residents and community organizations were instrumental in bringing the issue to light and calling for action.
Government Reaction: The reaction from neighborhood and state specialists was at first sluggish and insufficient. The official recognition of the crisis and the implementation of emergency measures took several months. In the end, the state and federal governments got involved and provided support for public health, infrastructure repairs, and water testing.
Political and legal repercussions:
Criminal Convictions: Numerous investigations and legal actions followed the crisis. A few authorities, including state and neighborhood government representatives, had to deal with criminal penalties connected with the misusing of the emergency and the inability to safeguard general wellbeing.
Arrangements for Money: To compensate Flint residents for their losses, legal settlements and compensation packages were formulated. Medical care, infrastructure maintenance, and other relief efforts received financial support.
Improvements and Infrastructure:
Pipe Substitution: The replacement of lead and galvanized steel pipes throughout Flint’s water system was one measure taken to address the problem. The ongoing process of replacing pipes is a significant investment in infrastructure repair.
Improvements to the water’s quality: Water quality was improved through enhanced testing, increased treatment, and alterations to the chemistry of the water to stop further corrosion.
Lessons Learned and Successes Increased Public Awareness and Changes to Policies:

Changes to the law: The Rock water emergency provoked changes in water the executives arrangements and guidelines. New norms and practices were acquainted with forestall comparative emergencies, including stricter necessities for erosion control and expanded straightforwardness in water testing.
Enhanced Observation: The emergency featured the requirement for further developed observing and oversight of water quality and foundation. To protect the public’s health, more stringent testing procedures and improved regulatory frameworks have been implemented.
Advocacy and resilience in the community:
Efforts from the Basis: The crisis demonstrated the effectiveness of community advocacy and grassroots activism in dealing with public health crises. Nearby pioneers, activists, and associations assumed a significant part in requesting responsibility and driving change.
Public Participation: A positive outcome of the crisis has been an increase in public involvement in environmental and water management issues. When it comes to addressing potential threats to public health, communities are more observant and proactive.
Restoring Confidence:
Bringing Confidence Back: In the wake of the crisis, a major focus has been on restoring residents’ trust in the authorities. Endeavors to draw in with the local area, give exact data, and address concerns have been fundamental for reestablishing trust in the water supply and government foundations.
Inequities and Disparities: Challenges and Criticisms
Financial Elements: The water crisis in Flint brought to light the existing disparities and inequities in infrastructure and public health. The emergency excessively impacted low-pay and minority networks, highlighting the requirement for impartial strategies and assets.
Systemic Breakdowns: The crisis revealed systemic shortcomings in emergency response, regulatory compliance, and government oversight. Preventing future crises in public health necessitates dealing with these systemic issues.
Long haul Wellbeing Effects:
Constant Health Problems: The drawn out wellbeing effects of lead openness are a critical concern. Tending to the wellbeing needs of impacted people, especially kids, needs continuous help, observing, and intercession.
Rehabilitation and recuperation: The residents of Flint face a challenging recovery and rehabilitation process that necessitates ongoing efforts to address both immediate and long-term health and environmental issues.
Future Directions: Strengthening Oversight and Regulation:
Further developed Guidelines: For the purpose of preventing crises of a similar nature, strengthening regulations and oversight of infrastructure and water quality are essential. Upgraded principles for erosion control, water treatment, and framework support ought to be focused on.
Straightforwardness and Responsibility: For effective oversight and public trust, water management practices and decision-making processes must be more transparent and accountable.
Putting money into infrastructure:
Redesigning Frameworks: Putting resources into the modernization and support of water framework is fundamental for guaranteeing protected and dependable water supplies. Continuous endeavors to supplant obsolete lines and further develop water treatment offices are vital for long haul strength.
Reasonable Arrangements: Innovative technologies and methods, as well as sustainable approaches to water management, can aid in addressing current and future issues.
Supporting Impacted People group:
End
Social and Health Services: Giving exhaustive wellbeing and social administrations to impacted networks is essential for tending to the drawn out effects of the emergency. Medical care, educational programs, and community resources should all be part of support services.
Community Participation: Participating with affected communities in the formulation of policies and decision-making processes can assist in ensuring that their requirements and concerns are adequately addressed.



GIPHY App Key not set. Please check settings