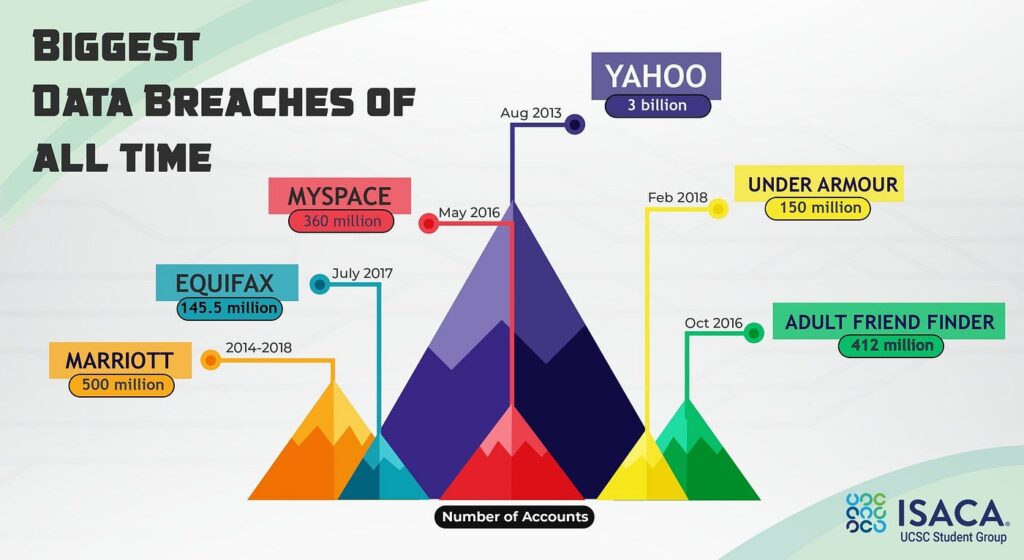
With over 3 billion user accounts affected, the Yahoo’s data breach is one of the most significant cybersecurity incidents in history. These breaches, which occurred between 2013 and 2014, revealed significant security flaws in Yahoo’s infrastructure. The specifics of the breach, Yahoo’s response, and the broader repercussions for corporate governance and cybersecurity are the subject of this case study.
Overview of the Firm:
Yahoo! Inc. Yahoo was once a major internet company that was well-known for its web portal, search engine, and email services. It was established in 1994 by Jerry Yang and David Filo. Yahoo had become a major player in the technology and media industries by the beginning of the 2000s.
Service Collection: Yahoo’s products included, among others, Yahoo Sports, Yahoo Finance, Yahoo Mail, and Yahoo News. Yahoo was one of the most popular websites worldwide at its height.
The breach was found:
First Reports: In September 2016, Yahoo announced that 500 million user accounts had been compromised in a data breach. Yahoo revealed in December 2016 that a separate breach in 2013 had compromised 1 billion accounts, resulting in a total of 3 billion affected accounts across both incidents. At first, the breach was thought to be isolated.
Information on the Breach:
The Kind of Breach:

Access Without Permission: Unauthorized access to Yahoo’s user database was the cause of the breaches. Names, email addresses, phone numbers, and birth dates—as well as encrypted passwords in some cases—were among the sensitive user data that the attackers obtained.
Security At Risk: Yahoo’s hashing algorithms were out of date, making it easier for hackers to decrypt the passwords in the stolen data, which included encrypted hashed passwords.
Methods and Perpetrators:
Attribution: Although Yahoo did not specify which nation-state was responsible for the breaches, it claimed that they were caused by a state-sponsored actor. It was believed that sophisticated cybercriminals with substantial resources were responsible for the breaches.
Exploited Weaknesses: The attackers took advantage of security holes in Yahoo’s systems. The breaks included progressed procedures, including phishing and social designing, to acquire unapproved access.
Yahoo’s Answer:
Transparency and Communication:

Public Notification: There was a delay in Yahoo’s public disclosure of the breaches. Despite discovering the breach in 2014, the company did not disclose it until late in 2016. September 2016 saw the disclosure of the breach from 2014.
Notification to Users: Yahoo offered advice on how to secure their accounts and advised affected users to change their passwords. In addition, the business put in place additional security measures, such as improved encryption protocols.
Financial and legal repercussions:
Investigations into Regulations: Regulations, such as the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), began looking into the breaches. Yahoo’s handling of the breach and whether or not it adequately and promptly disclosed the breach to investors and users came under scrutiny.
monetary impact: A decline in Yahoo’s market value was one of the significant financial consequences. The breaches had an impact on Yahoo’s negotiations for acquisition, particularly with Verizon Communications, which ultimately purchased Yahoo’s core internet operations in 2017 at a lower price.
Governance and accountability in the workplace:

Changes in leadership: Yahoo’s leadership and governance practices came under more scrutiny as a result of the breaches. Marissa Mayer, CEO at the time of the breaches, was criticized for how she handled the situation.
Examining the inside: Yahoo revamped its cybersecurity infrastructure and carried out an internal audit of its security procedures.
Implications and Effects:
Awareness of security issues:
Increased Attention to Safety: The Yahoo data breach brought to light the significance of comprehensive cybersecurity measures. Strong encryption, regular security audits, and prompt disclosure of breaches became increasingly important security practices for businesses.
Changes to regulations: Data protection laws and standards have become more stringent as a result of the breaches. For instance, the 2018 General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) of the European Union places a greater emphasis on prompt breach notification and accountability for data breaches.
Respect and Credibility:
User skepticism: Yahoo’s reputation and user trust were significantly impacted by the breaches. Users, investors, and observers of the industry voiced their displeasure at the delayed disclosure and handling of the breaches.
Effect on Purchasing: Yahoo’s valuation and Verizon’s acquisition of it were affected by the breaches. The diminished value of Yahoo’s internet assets as a result of the breaches was reflected in the decrease in the acquisition price.
What We’ve Learned:
Timely disclosure is crucial: The Yahoo case demonstrated how crucial it is to promptly notify users and regulatory bodies of breaches. In order to mitigate the effects of a breach and maintain trust, timely disclosure is essential.
Security investments: Encryption, regular security assessments, and plans for responding to incidents are all necessary security investments for businesses. Protecting user data necessitates ensuring that security protocols are up to date and effective.
Conclusion:
The Yahoo data breach is an important case study in corporate governance and cybersecurity. Yahoo suffered significant financial losses, a damaged reputation, and changes in regulatory practices as a result of the breaches. The incident emphasizes the significance of proactive cybersecurity risk management, timely disclosure, and comprehensive security measures. The lessons learned from the Yahoo data breach continue to be relevant in shaping efficient cybersecurity strategies and practices as organizations continue to face evolving threats.



GIPHY App Key not set. Please check settings