Eric Yuan founded Zoom Video Communications in 2011, and during the COVID-19 pandemic, the company went from being a niche video conferencing tool to a household name. Zoom’s growth strategies for scaling up to meet unprecedented demand, as well as the impact of this growth on the company’s future prospects, are the subject of this case study.
Overview of the Firm:
Beginnings and Development: Zoom was founded by Eric Yuan, a former Cisco engineer, with the goal of developing a user-friendly and high-quality video conferencing solution. When it first went public in 2013, the company aimed at businesses looking for a better communication tool.
Essential Merits: Video conferencing, webinars, screen sharing, and other collaborative tools are available on the Zoom platform. It quickly set itself apart from other competitors in the video conferencing market thanks to its ease of use, dependability, and feature set.
Position Prior to Pandemic:
Steady Progress: Zoom had been steadily expanding prior to the pandemic, with a focus on serving business clients. Although it had not yet reached the mass consumer market, it had established a solid reputation in the enterprise market.
Base of Users: Zoom’s popularity among educational institutions and businesses can be seen in the approximately 10 million daily meeting participants it had by the end of 2019.
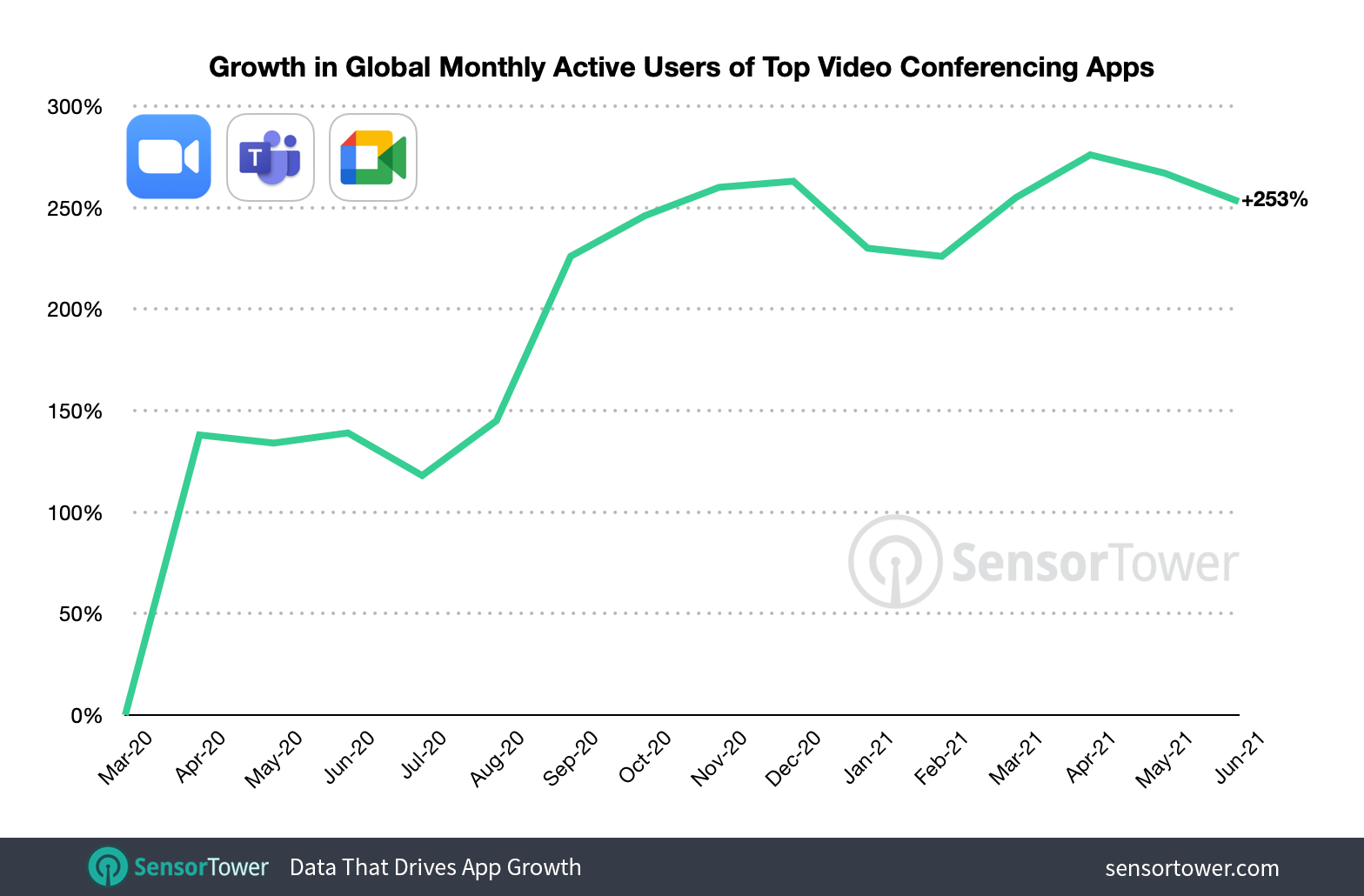
Growth Caused by the Pandemic:
Demand Increase:
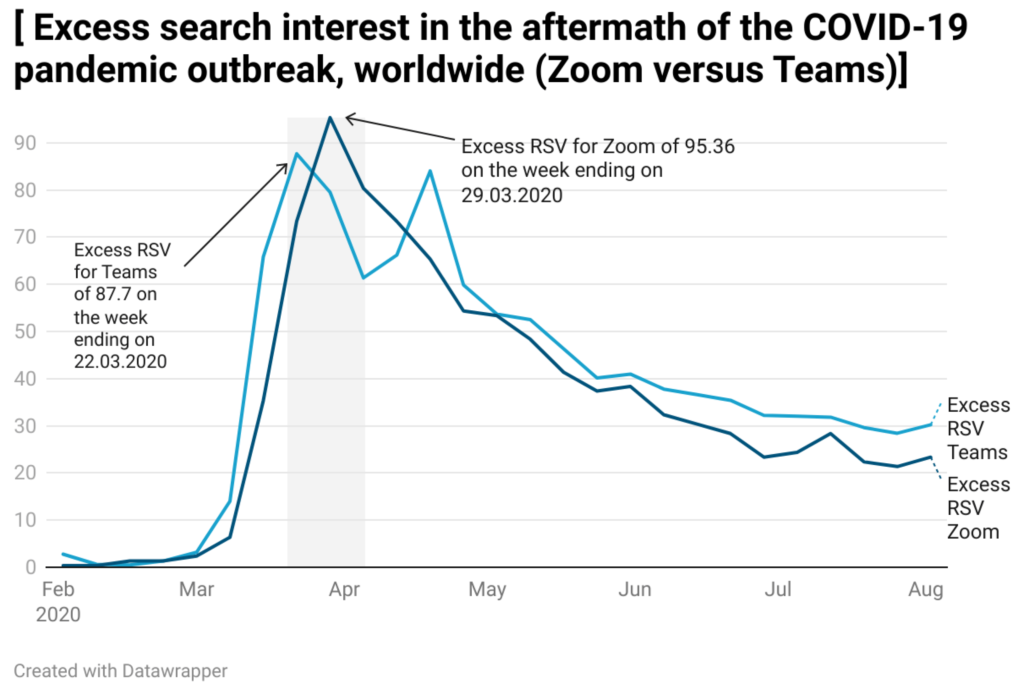
Impact of a pandemic: Beginning at the beginning of 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic resulted in widespread lockdowns and remote work arrangements. Virtual communication was quickly adopted by individuals, educational establishments, and organizations to maintain business operations, pursue education, and maintain connections.
Explosive expansion: The use of Zoom increased at an unprecedented rate. The platform had reached over 300 million daily meeting attendees by April 2020, a significant increase from pre-pandemic levels.
Infrastructure and scale:
Moving up: Zoom made significant investments in expanding its infrastructure to cope with the increase in demand. To accommodate the increased traffic and guarantee a dependable user experience, the company increased the capacity of its servers, upgraded its technology stack, and enhanced its security measures.
Expansion globally: In order to offer users around the world better performance and lower latency, Zoom expanded its global reach and expanded its data centers. The company was able to manage the increasing number of users and maintain service quality thanks to this expansion.
Strategic Solutions:

Enhanced Product Features:
New features: During the pandemic, Zoom improved and added a number of new features to meet changing user requirements. These included virtual backgrounds, enhanced security features, breakout rooms for group discussions, integrations with other productivity tools, and other features.
Health care and education: The company tailored its offerings to specific market segments, such as the healthcare and education industries. While Zoom for Healthcare supported telemedicine and remote consultations, Zoom for Education provided tools for virtual classrooms.
Privacy and security:
Taking Care of Concerns: Zoom was criticized for vulnerabilities and privacy issues as a result of the increased focus on video conferencing security. In response, the business made significant investments in security enhancements, such as improved meeting controls, end-to-end encryption, and additional security features.
Compliance and Transparency: Through transparency and adherence to global data protection regulations, Zoom worked to address concerns. The company took steps to comply with regulations like the CCPA and GDPR.
Customer and Community Engagement:
Assistance for Workers in the Field: During the pandemic, frontline workers, educational institutions, and non-profits received complimentary access to Zoom’s platform to meet their requirements for remote work and communication.
Customer Service: To accommodate the increased number of customers, the company enhanced its customer support capabilities. To assist users in effectively navigating the platform, Zoom provided resources, instructional videos, and devoted support teams.
Results and Impact:
Place in the Market:
Gaining more market share: During the pandemic, Zoom’s expansion solidified its position as a leading platform for video conferencing. Overtaking rivals like Microsoft Teams and Google Meet, the company’s market share in the video conferencing sector increased significantly.
Educating the Public: Zoom’s brand became more well-known as a result of the pandemic, which made it a household name. The platform’s widespread adoption was facilitated by its reliable and user-friendly interface.
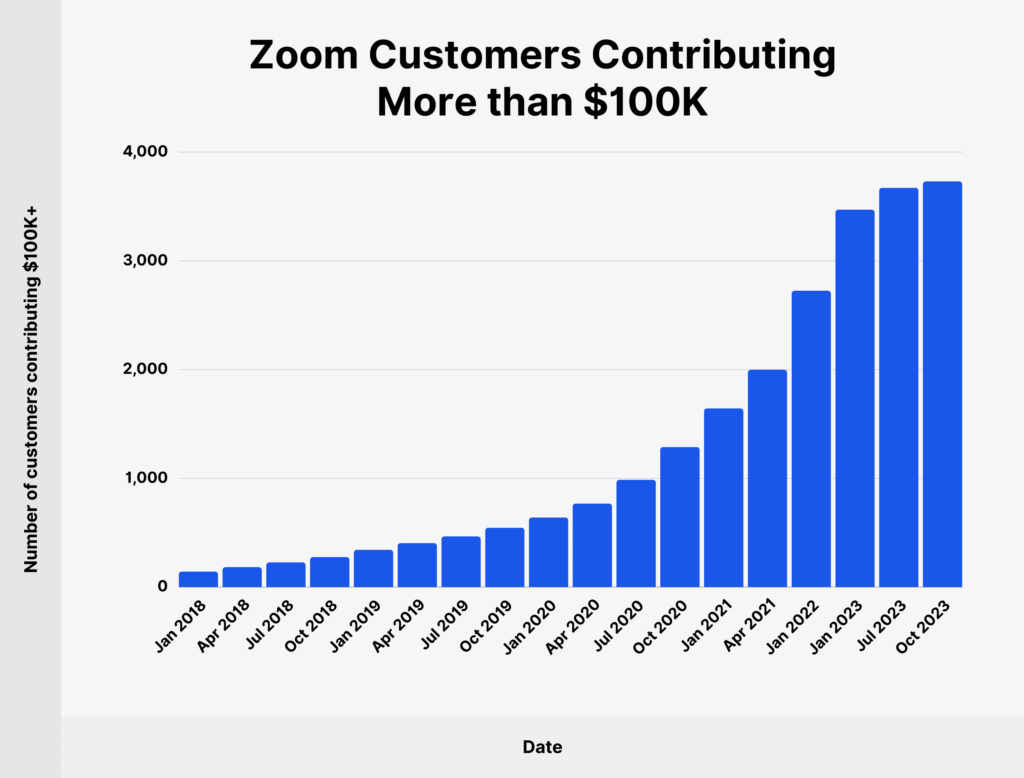
Financial Results:
Increasing Revenue: During the pandemic, Zoom’s revenue increased significantly year over year, the company reported. Zoom’s revenue for the fiscal year 2021 was $2.65 billion, a significant increase from the previous year.
Success on the stock market: The performance of the company’s stock market reflected its financial success. During the pandemic, Zoom’s stock price skyrocketed, making it one of the best tech performers.
Future Perspectives:
Keeping Growth Alive: Zoom faces the challenge of maintaining its growth and competitive edge as the world moves into a post-pandemic environment. The company is concentrating on exploring new market opportunities, enhancing the user experience, and expanding its product range.
Model of Hybrid Work: Long-term opportunities have emerged for Zoom as a result of the shift toward hybrid and remote work models. By providing services that facilitate both in-office and remote collaboration, the company is establishing itself as an important player in the workplace of the future.
What We’ve Learned:
Scalability’s Importance:

Investing in Infrastructure: The significance of making investments in infrastructure that is scalable is demonstrated by Zoom’s capacity to rapidly expand in response to a sudden increase in demand. In order to maintain service quality and deal with unexpected spikes in usage, businesses must be prepared.
Meeting the Needs of Users:
Feature Creation: The pandemic demonstrated the significance of ongoing product development and modification to meet shifting user requirements. Zoom’s ability to rapidly introduce new features and address emerging requirements was the driving force behind its success.
Taking Care of Security Concerns:
Security Measures Taken Ahead: In order to maintain credibility and trust, it is essential to ensure the privacy and security of user data. Zoom’s efforts to address security issues and protect its reputation and user confidence were crucial.
Conclusion:
Zoom’s rapid growth during the COVID-19 pandemic is evidence of the company’s adaptability, creativity, and capacity to meet unprecedented challenges. Zoom’s rise to global dominance of the video conferencing market demonstrates the impact of digital transformation on communication and collaboration. The company continues to play a crucial role in shaping the future of work and connectivity as it navigates the post-pandemic landscape.



GIPHY App Key not set. Please check settings